White Papers
PROVEN TECHNOLOGIES AND REMEDIES GUIDANCE
The Department of Toxic Substances Control (DTSC) is issuing this Proven Technologies and Remedies (PT&R) guidance document for immediate use on cleanups at hazardous waste facilities and Brownfields sites.
Gene Expression Factors
REMEDIATION of PETROLEUM and CHLORINATED HYDROCARBON CONTAMINATED SOILS UTILIZING GENE EXPRESSION FACTORS (FACTOR)
The Remedial Process -
The Stockholm Twelve, also known as the “Dirty Dozen”
The chemical industry’s process of chlorinating a product,
The chemical industry’s process of chlorinating a product,

are persistent organic pollutants (POPs) that have been proven to cause varying degrees of harm to man or the environment. Many of the nearly one million polluted sites in the United States today are impacted by one or more of these toxic chemical pollutants. Aldrin, chlordane, DDT, dieldrin, endrin, heptachlor, hexachlorobenzene, mirex, toxaphene, hexachlorobenzene, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDD/PCDF) are widely accepted as the worst of the worst environmental pollutant due to the pollutant’s toxicity and persistence. These 12 pollutants share a chlorinated structure like that of the PCB molecule.
The chemical industry’s process of chlorinating a product,
The chemical industry’s process of chlorinating a product,
The chemical industry’s process of chlorinating a product,

such as an insecticide or a herbicide, began in the 1940’s in response to the farmer’s need for weed and insect controls that could withstand weathering. By chlorinating pesticides, insecticides became far more effective in controlling the target insects and herbicides became more effective weed killers. Unfortunately, the chlorination process also creaed a a class of toxic pollutants that are highly resistant to natural breakdown.
Decades of research has shown that the persistence of these pollutants, more than acute toxicity, is the principal contributing factor to the pollutant’s adverse physiological impact on both vertebrate and invertebrate species. Each of the 12 POPs is a known or suspected carcinogen and/or endocrine disrupter.
With the goal of promoting enzymatic
Following the incorporation of BioBlend
Following the incorporation of BioBlend

dechlorination of POPs in an aerobic condition, the developers of the BioBlend first focused on the highly persistent insecticide, toxaphene. The toxaphene molecule is like that of the PCB molecule in that it’s a highly chlorinated structure. In the absence of the eight chlorine attachments, toxaphene is converted to camphene, which is readily destroyed by the naturally occurring (indigenous) bacteria in the soil. Biotech’s BioBlend product line is designed to perform the critical function of enhancing the production of reductive enzymes within the soil’s indigenous bacterial population.
Following the incorporation of BioBlend
Following the incorporation of BioBlend
Following the incorporation of BioBlend

into the impacted soil, the indigenous bacterial population increases rapidly to a level where bacteria compete for available carbon. Now able to produce and secrete reductive enzymes, the goal of enzymatic dechlorination is achieved as the bacterial enzymes cleave the chlorines from the molecule. The liberated chloride ions attach to the organic matter in the soil as a simple salt or are harmlessly off-gassed to atmosphere. In laboratory studies on treated soil, evidence of enzymatic dechlorination is demonstrated by chloride ion production over time.
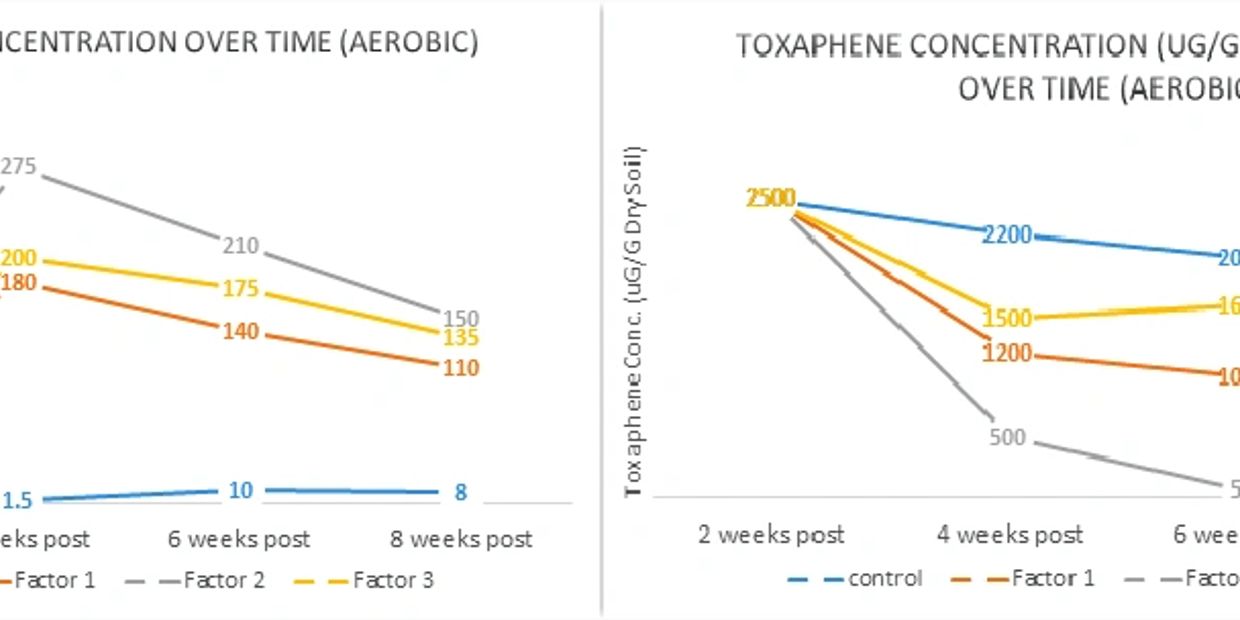
As the indigenous soil bacteria begin to dechlorinate the molecule, chloride ion production spikes and then levels off as the microbial population perform the task for which they were designed, to convert organic carbon for mineralization (cell growth) and reproduction. As illustrated above, a corresponding decrease in toxaphene concentrations in the treated soil is evidenced as the molecule is dechlorinated and the camphene constituents are utilized by the indigenous bacteria.
In 2012, a bench study was performed in cooperation with EPA Region 4 on toxaphene impacted soil collected from the Woolfolk Chemical Superfund site in Ft Valley, Georgia. The purpose of this study was to determine if toxaphene congener reductions were occurring concurrently with the dechlorination and destruction of the parent toxaphene molecule. The table above illustrates that following a single application of BioBlend, significant reductions in toxic congeners occur concurrently as the parent molecule is dechlorinated and the organic constituent compounds are utilized by the indigenous soil bacteria.
The metabolic pathway by which the Stockholm 12 POPs are destroyed remains consistent throughout the spectrum of persistent chlorinated pollutants with pesticides on the less recalcitrant end of the spectrum, PCBs falling in the middle, and dioxins and furans occupying the most recalcitrant position on the spectrum. In bench studies and in commercial applications, soils impacted by chlorinated pesticides, PCBs, dioxins, and furans have been successfully remediated, to within regulatory cleanup standards.
Learn More
Click below for an overview of Biotech’s environmentally safe, effective and lower cost alternative to restoring your polluted site to a condition suitable for human, animal, and plant habitation and use.
Rethinking Clean from the Ground Up
Copyright © 2000-2023 - All Rights Reserved
BIOTECH RESTORATIONS, LLC